
UPDATE 1st June: The European Board of Medical Assessors (EBMA) has recently announced that its next conference will take place on 11th - 14th April 2024 at the University of Plymouth. The theme for the event is “The Future of Assessment in Medical Education: Opportunities and Threats” and promises to be a much-valued opportunity for those involved in assessment in medical education to meet, learn, and share their experiences. Further information on key note and plenary speakers as well as the provisional programme will be soon available. The Practicum Foundation, which signed a partnership agreement with EBMA by the end of 2021, envisages to provide up-to-date information on the Practicum Script clinical reasoning training programme at undergraduate level.
After a sharp psychometric analysis conducted by the psychometrician of the European Board of Medical Assessors (EBMA) Carlos Collares, Practicum Script has been backed up in terms of validity, reliability, and acceptability. The annual conference of EBMA, held in Helsinki (Finland) from the 10th to the 12th of November, was the opportunity to share this good news with a short communication delivered by Prof Collares, who left a take home message: “Practicum Script can contribute to improve the clinical care decisions of future physicians by helping students to develop effective thinking skills to deal with complexity and ambiguity in clinical practice.”
Helsinki - November 15, 2022. Each year the EBMA conference is a much-valued opportunity for those involved in assessment in medical education to meet, learn, and share their experiences. This year Practicum Script announced the psychometric results of its application at undergraduate level. The findings support the conclusion that “Practicum Script is a useful resource to help students strengthen their clinical reasoning skills and their ability to manage uncertainty in clinical practice, with evidence of reliability and validity, in addition to a high level of acceptability”. Prof Carlos Collares took the floor in a morning intervention on Saturday the 12th of November.
In a call centred on “Paradigms in Assessment”, EBMA welcomed the work done together with the Practicum Foundation, which is the integral developer of the Practicum Script clinical reasoning simulator, to develop effective approaches tailored towards the development of clinical thinking skills. According to Prof. Collares, “there are currently no standardised approaches for assessment of clinical reasoning skills, and Practicum Script represents a unique opportunity to address cognitive training and its measurement.”
According to Prof. Collares introduction, Practicum Script is an innovative educational e-solution targeting medical students, and formerly CME/CPD. It is designed to foster users’ reasoning and expertise development through challenging clinical cases in which expert clinical judgments often diverge. The model features a comprehensive assessment of different stages of decision-making skills, from hypothesis generation to hypothesis evaluation, involving a probabilistic approach, a feedback model based on experts’ opinion, and evidence-based medicine, as well as an ongoing clinical debate among participants.
The investigation focuses on the data reunited across the international multicentre study known as Practicum Universities. “The methodology was simple: 1) individual response of the 20 clinical cases composing the proposal, 2) assessment of students’ satisfaction and perceptions about potential benefits of Practicum Script and 3) data analysis”, Prof Collares detailed. Almost 2,500 medical students (2,457) from 21 medical schools took part on a voluntary basis in this huge effort to investigate the feasibility of using Practicum Script as a clinical reasoning training methodology in undergraduate teaching and assessment.
As for the students’ engagement, 1,502 students (61% out of the original 2,457) completed the pilot and 89,5% of a consistent sample of them (n=380) rated the experience as excellent or highly satisfactory, while 82,1% expressed their willingness to incorporate the methodology in their plan of studies. In a survey, students valued Practicum Script as a good simulation model relevant to their future practice and especially convenient for self-directed learning. In general, they agreed it helps with the transfer of theoretical knowledge into real-life situations.
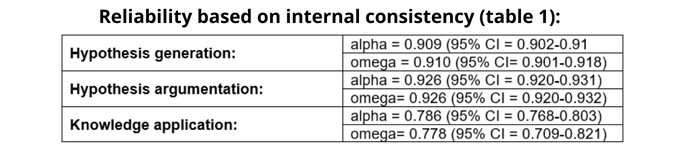
Data analysis
Items of Practicum Script were classified in three dimensions: hypothesis generation (HG), hypothesis argumentation (HA), and knowledge application (KA).” Estimates of reliability were calculated using Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients, and validity based on internal structure was obtained by confirmatory factor analysis (CFI, TLI, RMSEA, SRMR). Also, items from the KA domain were analysed using cognitive diagnostic modelling (CDM), which Prof Collares highlights that means “a Q-matrix, based on the type of cognitive attributes needed for the resolution of the items, was created and validated using the method percentage of variance accounted for (PVAF).”
The reliability estimates for the three sections were high, with narrow confidence intervals and Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega yielding similar values (table 1). Confirmatory factor analysis revealed acceptable goodness-of-fit indices for the three-factor model (CFI = 0.95; TLI = 0.94; RMSEA = 0.03, SRMR = 0.05). The model showed moderate to high significant correlations between the constructs measured by the test, with a coefficient of 0.83 for the correlation between HG and HA, a coefficient of 0.75 for the correlation between HG and KA and a coefficient of 0.71 for the correlation coefficient between HA and KA.
For Collares, “CDM analysis of the KA items resulted in a good absolute test fit in terms of RMSEA (0.05) and SRMR (0.09).”
The results of this study demonstrated a high level of reliability for the three sections of Practicum Script (HG, HA, KA) and evidence of the programme’s validity based on its internal structure and response processes. In the words of Prof Collares, “given the high levels of acceptability, validity and reliability of Practicum Script, one can infer that it has a high level of educational utility for undergraduate students to develop their clinical reasoning skills and for teachers and institutional stakeholders to assess clinical reasoning skills in their undergraduate students.”
Our personalized help center enables you to obtain technical support and help for navigating through the site and using the program.